#paeds
see: [RCH supracondylar fracture](https://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/guideline_index/fractures/Supracondylar_fracture_of_the_humerus_Emergency_Department/) → [Supracondylar fracture clinic](https://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/guideline_index/fractures/Supracondylar_fracture_of_the_humerus_Outpatient_fracture_clinics/)
- [Schwartz emergency radiology Supracondylar fractures](x-devonthink-item://2A71AF1A-4715-4D5F-9841-03401D8E6C4E?page=250&start=2259&length=23&search=Supracondylar%20Fractures)
see also: [[paediatric elbow#CRITOE]], [[Neurovascular assessment]], [[Soft tissue signs of a fracture]], [[paediatric elbow#Anterior humeral line]]
> [!key points]
> - ==neurovascular risks==: brachial artery, **anterior interosseous nerve** (AIN), *median nerve*. rarely *ulnar* or radial nerve
> [!warning] Indications for urgent ortho review
> - absence of radial pulse
> - ischaemia of hand (pale, cool)
> - skin buckering or anterior bruising
> - open injury
> - neurological injury
![[Pasted image 20240515174653.png]]
![[Pasted image 20240515175513.png|anterior interosseous nerve anatomy, most common nerve injury]]
![[Pasted image 20240515181709.png]]
# Mechanism
can be from FOOSH
![[Pasted image 20250124004648.png]]
# Gartland classification
| **Gartland classification for extension fractures** | **ED management** | **Follow-up** |
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| ![[Pasted image 20240515181419.png]]<br>non-displaced fracture<br><br>![[Pasted image 20250124003959.png]] | ==check [[paediatric elbow#Anterior humeral line\|anterior humeral line]] for evidence of posterior displacement==<br><br>Immobilisation in an above-elbow backslab in 90 degrees elbow flexion with sling for 3 weeks. The backslab and sling should be worn under clothing (e.g. loose fitting shirt) and not through the sleeve<br><br><br>**TIP**: Avoid putting on a short, flimsy backslab. The backslab should extend as high above the elbow as possible (i.e. close to the axilla) and down to the metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) joints.<br><br>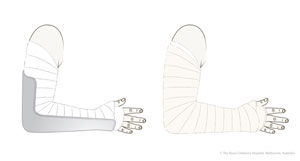 | Give parent [undisplaced supracondylar fracture fact sheet](https://www.rch.org.au/uploadedFiles/Main/Content/ortho/supracondylar_elbow_fracture_undis_vpon.pdf "Undisplaced_supracondylar_fact_sheet") <br><br>Undisplaced fractures can be followed up with the GP in 3 weeks. Repeat x-ray is not required. |
| ![[Pasted image 20240515181444.png]]<br><br>![[Pasted image 20230825214340.png]]<br>Angulated fracture with intact posterior cortex | Refer to the nearest orthopaedic on call service for advice<br><br>A gentle reduction can be achieved by an anterior push on the distal fragment as the elbow is flexed to 90 degrees<br><br>Note the exception is type II injuries with coronal plane deformity (see radiological assessment). These must always be managed by orthopaedics | Observation overnight<br><br>Fracture clinic within 7 days post-injury with x-ray of distal humerus in backslab |
| ![[Pasted image 20240515181548.png]]<br><br>Displaced distal fragment posteriorly, no cortical contact | Refer to the nearest orthopaedic on call service<br><br>Requires urgent reduction and percutaneous pin fixation | To be organised by orthopaedic service |
# Assessment
- pain
- anterior bruising indicates more severe injury
- [[Neurovascular assessment|neurovascular]] status
- skin tethering
- for subtle XRs, review [[paediatric elbow#Anterior humeral line|anterior humeral line]] on XR to look for subtle posterior displacement
![[Pasted image 20250124004724.png]]
![[Pasted image 20250124004758.png]]
# Complications
- Short term:
- brachial artery damage
- can lead to compartment syndrome or volkmann's ischemic contracture
- higher risk with higher grade fracture
- neurological: median, ulnar, or radial nerve damage
- **most common is **anterior interosseous nerve palsy** (branch of *median nerve*), followed by *median nerve*, *ulnar nerve*, and less commonly radial nerve palsy**
- ==cannot make OK sign==
- Because there is no sensory component to the anterior interosseous nerve, the injury can only be identified through motor testing by making the “OK” sign
- majority do resolve. if deficit noted after theatre, need to go back to theatre
- [[Compartment syndrome]]
- long term:
- malunion (gunstock deformity/cubitus varus) can result from tilt in the coronal plane
- normal carrying angle of arm reversed causing the forearm to deviate abnormally to the midline when the elbow is extended
- more of a cosmetic effect than functional effect
- volkmann's ischaemic contracture of forearm
- Occurs through vascular compromise at the time of injury, causing the death and ultimately fibrous contraction of the affected muscle. Typically the fingers, thumb and wrist become fixed in flexion
- Refusal to open the hand, pain with passive extension of the fingers, and forearm pain out of proportion to exam findings are signs of impending Volkmann’s ischemia
- myositis ossificans
# Treatment
see table above for management of low-grade supracondylar fractures
## reduction
- reduce displaced supracondylar fracture
- see [Rosen Fig 170.16](x-devonthink-item://FF94D29F-11D4-4772-A837-75306C2A9A97?page=5&start=266&length=11&search=Fig.%20170.16)
![[Pasted image 20240515181907.png]]
# Related Questions
## elbow xr
- [ ] 3Q: [Elbow injury](x-devonthink-item://80040649-2DDB-4266-9A7C-4DE4E6DD4AE6?page=8) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://C96EDD2F-137A-43E5-80EE-5F42C5971D55?page=11) -- [prop](x-devonthink-item://51B63B5B-D684-4BF3-8B62-95FCA5EF7503?page=10)
- [x] DUPLICATE Q: [Elbow injury](x-devonthink-item://1A2C485F-D4AD-4821-AFF2-452BA753717F?page=6) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://FD716379-1A77-4B5B-B257-1154995ECA6E?page=2)
- [ ] 4Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://7FCD3940-4BB4-45FE-86A6-E5707E82D5B5?page=67) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://3263A68A-96A6-43EC-985B-43260C3509BF?page=25)
- [ ] 5Q: [Elbow injury](x-devonthink-item://1442A590-B32E-40BE-9C29-6401A71DC2DC?page=17) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://0C9617AB-8E16-4A75-ADF0-AB06FA726B0A?page=7) -- [prop](x-devonthink-item://D5D52721-F021-4ABC-B6EA-727BF54DF6B9?page=5)
- [ ] 6Q: [Elbow injury](x-devonthink-item://5FC539E5-7F1D-48E5-B062-83009DA98093?page=16) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://D25C2F83-6C30-4F45-8B5B-6E7E57BD24A3?page=8) -- [prop](x-devonthink-item://0F9688C6-AA10-45DA-BFF4-9BBBFC201582?page=6)
- [ ] 7Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://2504F01B-CEAF-41E8-803B-B3AE1B07A49E?page=15) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://00427DF6-6D28-4FEB-A0CA-DF96DBBBCE97?page=29) -- [prop](x-devonthink-item://AB9BDA6D-9CA8-4E73-9D15-B6105225A1B4?page=14)
- [x] 8Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://93BBB26D-55F3-43AF-A3B9-F829BE210561?page=15) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://E3D816B5-653D-4DC6-A389-8C69022A6062?page=12) -- [prop](x-devonthink-item://42954006-1F26-4D23-93DB-6738A8FA6D94?page=6)
- [ ] 9Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://40193B7A-D362-4C39-9D2A-2D112B58104B?page=22) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://AADB7978-B533-4E12-B6E4-E994C0B685FF?page=20) -- [prop](x-devonthink-item://F8FBC1E8-52B3-47B9-8EBB-5CB6F3F81EBC?page=10)
- [ ] 10Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://87BC05C2-0A6B-436D-B51A-75E14AA5EA7E?page=4) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://98D17FA0-225B-4E94-B21C-4E36D5C76A7C?page=54) -- [prop](x-devonthink-item://093F49C6-2E32-460E-9C00-3E9F15CD417E?page=23)
- [ ] 11Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://7061D1B4-0AB9-4963-B3B0-23BDD975B2CD?page=42) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://3F30C77E-E23E-4200-89FE-48A41618E0C2?page=28)
## supracondylar fracture
- [x] 13Q: [Elbow injury](x-devonthink-item://F0498813-9350-484C-AD5B-6FF7C3AE9015?page=19) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://A491A3F6-FD6D-492F-BCBE-7F7BAE101EDF?page=18)
- [x] DUPLICATE Q: [Elbow injury](x-devonthink-item://1442A590-B32E-40BE-9C29-6401A71DC2DC?page=17) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://0C9617AB-8E16-4A75-ADF0-AB06FA726B0A?page=7)
- [x] DUPLICATE Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://93BBB26D-55F3-43AF-A3B9-F829BE210561?page=15) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://E3D816B5-653D-4DC6-A389-8C69022A6062?page=12)
- [ ] 14Q: [Supracondylar Fracture](x-devonthink-item://0987D972-A221-4F8A-B7D7-B0DCC349A2B3?page=16) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://C7FCB01A-E668-44AF-8C95-C298A40F8D68?page=12)
- [x] DUPLICATE Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://87BC05C2-0A6B-436D-B51A-75E14AA5EA7E?page=4) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://98D17FA0-225B-4E94-B21C-4E36D5C76A7C?page=54)
- [x] DUPLICATE Q: [Elbow Injury](x-devonthink-item://7061D1B4-0AB9-4963-B3B0-23BDD975B2CD?page=42) -- [Answer](x-devonthink-item://3F30C77E-E23E-4200-89FE-48A41618E0C2?page=28)
# OSCE
- [Cabrini supracondylar fracture](x-devonthink-item://AB413E88-3B94-4C96-B678-A944B89BC477)